electronics-journal.com
27
'25
Written on Modified on
TDK Introduces PLEC69B Thin-Film Inductors for AI Optical Transceivers
PLEC69B offers 10 μH in 1206 size, 70% lower DC resistance, 0.2 A rated current, and 10–200 MHz impedance range.
www.tdk.com

TDK Corporation has expanded its PLEC69B series (1.2 x 0.6 x 0.95 mm – L x W x H) of thin-film inductors, used for separating the data signal from the power in optical transceivers in AI data centers. Mass production of these components began in August 2025.
The widespread adoption of AI led to a skyrocketing demand for high-speed and high-capacity optical transceivers. Bias-tee circuits, which are used in these transceivers, are designed to superimpose signals and power on a single transmission line. Because of the impedance characteristics, inductors like the PLEC69B separate the signal from the power in bias-tee circuits, preventing the signal from flowing into the power side.
The new component achieves the highest standard performance* for an inductor with 10 μH in 1206 size with TDK’s proprietary metallic magnetic materials and structural designs. With a wide frequency range of 10 MHz to 200 MHz, signals can be separated from power with high impedance, which improves communication quality. Additionally, the DC resistance of 1.4 Ω (typ.) is approximately 70% lower than that of similar products on the market. This reduces power loss and heat generation. The rated current (Isat) of 0.2 A is also 1.7 times higher than that of similar products. In addition, the smaller dimensions require less space on the PCB. The PLEC69B ensures high reliability with an upper operating temperature limit of +125 °C.
TDK will continue contributing to its extensive lineup by developing products to meet market needs for lower power consumption and high-speed communications designed for data centers, servers, as well as optical communication devices and edge devices, supporting the AI market in anticipation of significant future growth.
*Source: TDK, as of August 2025
Glossary
- Bias-tee circuit: A circuit that superimposes and separates the signal and power along a single transmission line
Main applications
- For signal circuits: Bias-tee circuits for optical communication modules
- For power supply circuits: Smartphones, TWS, wearable devices
Main features and benefits
- High impedance characteristics with a wide frequency range of 10 MHz to 200 MHz
- DC resistance reduced by approximately 70%, producing a typical resistance of 1.4 Ω to help reduce power loss and heat generation
- Rated current (Isat) of 0.2 A, increased by 1.7 times
Key data
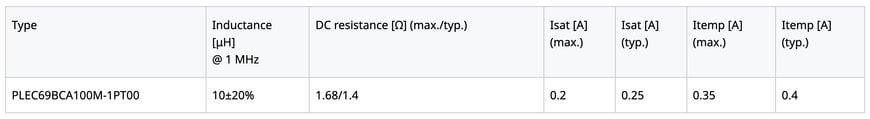
Isat: Current value based on inductance variation (30% lower than the initial inductance value)
Itemp: Current value based on temperature increase (temperature increase of 40 K by self-heating)
www.tdk.com

Isat: Current value based on inductance variation (30% lower than the initial inductance value)
Itemp: Current value based on temperature increase (temperature increase of 40 K by self-heating)
www.tdk.com

